Here is the list of top networking interview question 2018. The questions and answers available in this post are the most commonly asked question in a networking exam or in a computer networking interview.
Very Important Networking Interview Question 2018
Difference between LAN CAN MAN and WAN?
| LAN | CAN | MAN | WAN |
| LAN stands for Local Area Network | CAN stands for Campus Area Network | MAN stands for Metropolitan Area Network | WAN stands for Wide Area Network |
| Connects computers and workstations in office or home. | Connects two or more LANs within a campus | Interconnects network in a town or a city. | Connects geographically separated LANs. |
| Cover a local area of 1 KM. | Cover privately owned campus with an area of 5 to 10 KM. | Cover larger area then LAN but small area than WAN with an area or 2 to 100 KM. | Spans Large geographical area more than 100 KM. |
| Data transmission rate 10/100/1000 Mbps. | Data transmission rate is variable. | Data transmission rate is variable. | Data transmission rate is from 64Kbps to 150 Mbps. |
| Cheaper | Expensive then LAN | Expensive than LAN and CAN | Most Expensive |
| Uses IEEE 802 standard. | – | Uses IEEE 802 standard. | Uses ITU standard. |
| Networking devices such as repeater, hub and switch are used in LAN | Networking devices such as hub, switch and gateway are used. | Networking devices such as hub, switch, gateway and router are used. | Networking devices such as hub, switch, gateway and router are used. |
| Less Congestion | More congestion compare LAN | More congestion compare LAN and MAN | Most congestion network compared to LAN, CAN and MAN. |
Difference between hub, switch and router?
| HUB | SWITCH | ROUTER |
| Works in layer 1 (Physical layer) | Works in Layer 2 (Data Link Layer) | Works in Layer 3 (Network Layer) |
| Basically, use in Bus Topology | Basically use in Star Topology. | It is used to connect to different networks. |
| It broadcast data (sending data to all). | Switch is a multicast device. | Routers maintain routing table for data forwarding. |
| Hubs work only in half duplex mode. | Switches, unlike hubs, support full duplex. | Router supports full duplex. |
| If more than one device sends out data simultaneously then data collisions happen. | More than one device can send data. | More than one device can send data. |
| Switching protocols: PPP, PPTP, SLIP | Routing protocol: IP, IPSec, ICMP, IGMP, OSPF | |
| Hub cannot be configured. | Switch can be configured. | Router can be configured. |
| Hub is a device which transmits binary bits along networks. | Switch is a device which transmits frames along networks. | Router is a device which transmits data packets along networks. |
Difference between POP and IMAP?
| POP3 | IMAP |
| POP stands for Post Office Protocol | IMAP stands for Internet Message Access Protocol |
| POP3 port number is 110 and 995 (SSL) | IMAP port number is 143 and 999 (SSL) |
| This protocol is not synced with web server | This protocol is always in sync with the web server |
| To read the mail it needs to be downloaded first. | To read the mail it need not to be downloaded as you can access it online from the web server. |
| Mails can be accessed only from a single device. | Mails can be accessed from any device as you need to login to the web server. |
| The user cannot organize mails in the mailbox of the mail server. | The user can organize the emails on the server. |
| The user cannot create, delete or rename mailboxes on a mail server. | The user can create, delete or rename mailboxes on the mail server. |
| Any changes you make in the mail client (Outlook, Thunderbird) is not going to replicate to the web server. | Any changes you make in the mail client (Outlook, Thunderbird) it always replicates to the web server. |
| Mails are download in local PC and can be accessed locally without internet. | Mails are always on the server and it required internet to access them. |
Network protocols and their port number:
| Protocols | Port No |
| FTP | 21 |
| TELNET | 23 |
| HTTP | 80 |
| DNS | 53 |
| SSH (Secure Shell) | 22 |
| SMTP | 25 |
| DHCP Server | 67 |
| DHCP client | 68 |
| POP3 (Post Office Protocol, version 3) | 110 |
| NTP (Network Time Protocol) | 123 |
| IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) | 143 |
| SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) | 161 |
| IMAP3 (Internet Message Access Protocol 3) | 220 |
| SSL (Secure Socket Layer) | 443 |
| NetBIOS (Network Bios) | 139 |
| RIP (Routing Information Protocol) | 520 |
What is the color code of a straight-through cable?
| White of Orange | White of Orange |
| Orange | Orange |
| White of Green | White of Green |
| Blue | Blue |
| White Blue | White Blue |
| Green | Green |
| White of Brown | White of Brown |
| Brown | Brown |
What is the color code of a Cross over cable?
| White of Orange | White of Orange |
| Orange | Orange |
| White of Green | White of Blue |
| Blue | Green |
| White of Blue | White of Green |
| Green | Blue |
| White of Brown | White of Brown |
| Brown | Brown |
What is the color code of a Roll over cable?
| White of Orange | Brown |
| Orange | White of Brown |
| White of Green | Green |
| Blue | White of Blue |
| White of Blue | Blue |
| Green | White of Green |
| White of Brown | Orange |
| Brown | White of Orange |
Write the ranges of private IP Addresses.
| CLASS | Starting IP Address | Ending IP Address | Subnet Mask |
| A | 10.0.0.0 | 10.255.255.255 | 255.0.0.0 |
| B | 172.16.0.0 | 172.31.255.255 | 255.255.0.0 |
| C | 192.168.0.0 | 192.168.255.255 | 255.255.255.0 |
What is OSI Model?
Ans: OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection. It defines how data travels in a computer network. There are seven layers of OSI model:
· Application Layer
· Presentation Layer
· Session Layer
· Transport Layer
· Network Layer
· Data Link Layer
· Physical Layer
What’s the difference Between an Intranet and the Internet?
Ans: Internet
1. Internet is wide network of computers and is open for all.
2. Internet itself contains a large number of intranets.
3. The number of users who use internet is Unlimited.
4. The Visitors traffic is unlimited.
5. Internet contains different source of information and is available for all.
Intranet
Intranet is the generic term for a collection of private computer networks within an organization. An intranet uses network technologies as a tool to facilitate communication between people or work groups to improve the data sharing capability and overall knowledge base of an organization’s employees. It is like Ethernet.
1. Intranet is also a network of computers designed for a specific group of users.
2. Intranet can be accessed from Internet but with restrictions.
3. The number of users is limited.
4. The traffic allowed is also limited.
5. Intranet contains only specific group information.
Where do we use cross and standard cable?
Computer to computer ==> cross over
Switch/hub to switch/hub ==> cross over
Computer to switch/hub ==> straight over
Short Networking Interview Questions and Answer 2018
How many pins do serial ports have?
In computer it’s known as com port and could be available in 9pin or 25 pin. On router it has 60 pins.
What is public IP address?
A public IP address is an address leased from an ISP that allows or enables direct Internet communication.
What’s the benefit of subnetting?
Reduce the size of the routing tables.
Reduce network traffic. Broadcast traffic can be isolated within a single logical network.
Provide a way to secure network traffic by isolating it from the rest of the network.
What are the differences between static ip addressing and dynamic ip addressing?
With static IP addressing, a computer (or other device) is configured to always use the same IP address. With dynamic addressing, the IP address can change periodically and is managed by a centralized network service
What is APIPA?
Automatic private IP addressing (APIPA) is a feature mainly found in Microsoft operating systems. APIPA enables clients to still communicate with other computers on the same network segment until an IP address can be obtained from a DHCP server, allowing the machine to fully participate on the network. The range of these IP address are the 169.254.0.1 to 169.254.255.254 with a default Class B subnet mask of 255.255.0.0.
Which command will you use to find out the name of the pc in networks?
Ans: NSLOOKUP
Define Network?
A network is a set of devices connected by physical media links. A network is recursively is a connection of two or more nodes by a physical link or two or more networks connected by one or more nodes.
What is a node?
A network is an interconnection between two or more devices.
What is a Router?
A Router is a networking device which is used to connected two or more completely different network.
Name the factors that affect the performance of the network?
- Number of Users
b. Type of transmission medium
c. Hardware
d. Software
What is Protocol?
The protocol is a set rules used to communicate between the devices in a computer network
Define the terms Unicasting, Multicasting and Broadcasting?
If the message is sent from a source to a single destination node, it is called Unicasting.
If the message is sent to some subset of other nodes, it is called Multicasting.
If the message is sent to all the m nodes in the network it is called Broadcasting.
List the layers of OSI
- Physical Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Network Layer
- Transport Layer
- Session Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Application Layer
Which layers are network support layers?
- Physical Layer
b. Data link Layer and
c. Network Layers
Which layers are user support layers?
- Session Layer
b. Presentation Layer and
c. Application Layer
What is subnet?
A subnet is the sub division of a network. As for example, a network is divided into 3 sub networks. All these sub networks are called subnet.
What are the possible ways of data exchange?
(i) Simplex (ii) Half-duplex (iii) Full-duplex.
What is Brouter?
Brouter is a hybrid device that combine the features of both bridges and routers.
What is point-to-point protocol?
Ans: The interconnection between two devices without any other devices called Point-to-point protocol. As for example, two devices are connected to each other with a single cable is called point-to-point protocol.
What is MAC address?
MAC address is the physical address of a hardware device.
What is ICMP?
ICMP stands for Internet Control Message Protocol, a network layer protocol of the TCP/IP. Uses the echo test and reply the result whether a destination is reachable or not. PING command is the best example for ICMP.
What is difference between ARP and RARP?
The address resolution protocol (ARP) is used to translate IP address to MAC address.
The reverse address resolution protocol (RARP) is used to translate MAC address to IP address.
What is the minimum and maximum length of the header in the TCP segment and IP datagram?
The header should have a minimum length of 20 bytes and can have a maximum length of 60 bytes.
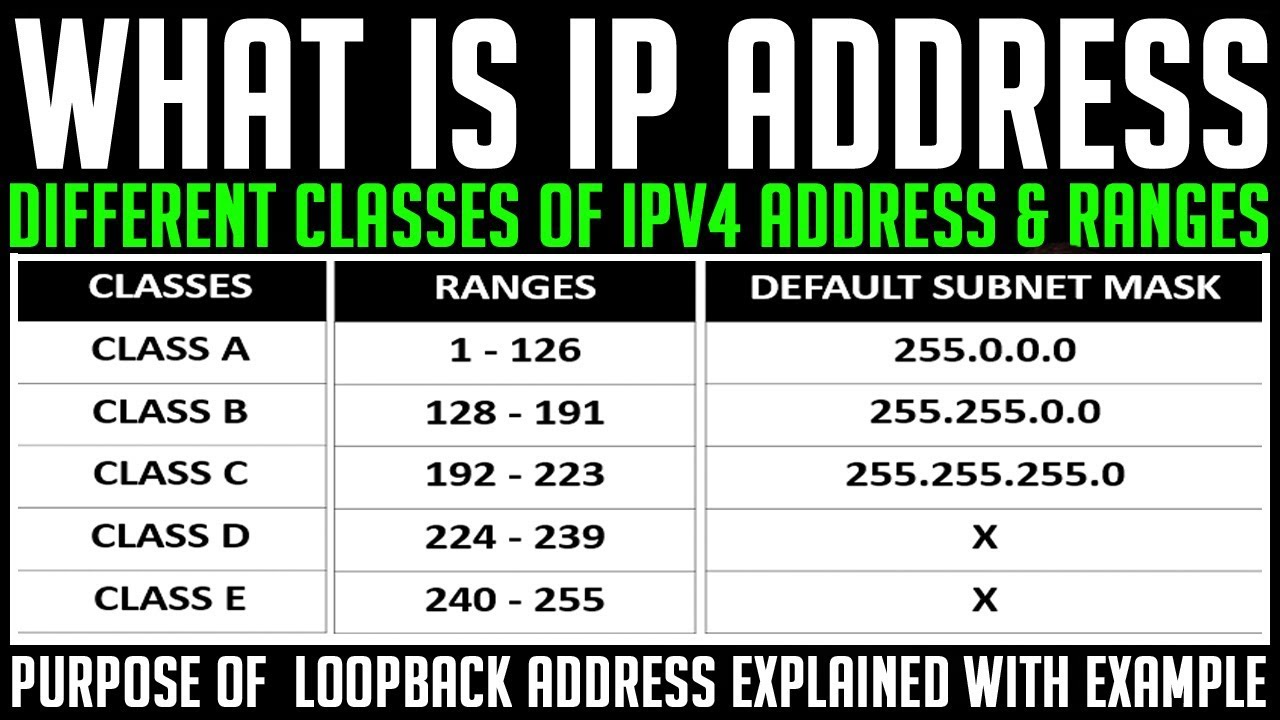
What is the range of addresses in the classes of internet addresses?
Class A – 1-126
Class B – 128-191
Class C – 192 – 223
Class D – 224 – 239
Class E – 240 – 254
What are the important topologies for networks?
- BUS topology: In this each computer is directly connected to primary network cable in a single line.
Advantages: Inexpensive, easy to install, simple to understand, easy to extend. - STAR topology: In this all computers are connected using a central hub.
Advantages: Can be inexpensive, easy to install and reconfigure and easy to trouble shoot physical problems. - RING topology: In this all computers are connected in loop. Advantages: All computers have equal access to network media, installation can be simple, and signal does not degrade as much as in other topologies because each computer regenerates it.
What is mesh network?
A network in which there are multiple routes for the data to travel is called mesh network.
What MAU?
In token Ring, hub is called Multistation Access Unit (MAU).
What is the difference between routable and non- routable protocols?
Routable protocols can work with a router and can be used to build large networks. Non-Routable protocols are designed to work on small, local networks and cannot be used with a router.
What is OSPF?
OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First. It is a routing protocol used to choose best and shortest route for the data to travel in a network.
What is RIP (Routing Information Protocol)?
It is a simple routing protocol used to exchange information between the routers.
Describe the POP3 protocol.
POP stands for Post Office Protocol. It is used to download a mail. The port number of POP3 is 110 and POP with SSL is 995.
Describe IMAP4 (Internet Mail Access Protocol) ?
IMAP stands for Internet Message Access Protocol. It is used to access the mail from multiple devices and it is always in sync to all the devices the mail is configured. The port number of IMAP is 143 and IMAP with SSL is 993.
Difference between POP and IMAP
| POP3 | IMAP |
| POP stands for Post Office Protocol | IMAP stands for Internet Message Access Protocol |
| POP port number is 110 and 995 (SSL) | IMAP port number is 143 and 999 (SSL) |
| POP is not sync with web server | IMAP is always sync with web server |
| To read the mail it has to be downloaded first. | To read the mail it need not to be downloaded as you can access it online from the webserver. |
| Mails can be access only from a single device in which POP is configured. | Mails can be access from any device as you need to login to the webserver. |
| The user cannot organize mails in the mailbox of the mail server. | The user can organize the mails on the server. |
| The user cannot create, delete or rename mailboxes on a mail server. | The user can create, delete or rename mailboxes on the mail server. |
| Any changes you make in the mail client (Outlook, Thunderbird) is not going to replicate to the web server. | Any changes you make in the mail client (Outlook, Thunderbird) it always replicate to the webserver. |
| Mails are download in local PC and can be access locally without internet. | Mails are always be in the server and it required internet to access them. |
| To read the mail it has to be downloaded first. | To read the mail it need not to be downloaded as you can access it online from the webserver. |
Differentiate between hub and switch.
- Hub is a layer 1 device while Switch is layer 2 device.
- Hub is a broadcast device (sending one to all) but Switch is a multicast device. (can be send to a particular device)
- You cannot configure hub but you can configure switch.
- Hub does not store the MAC address but Switch stores the MAC stores.
What are 10Base2, 10Base5 and 10BaseT Ethernet LANs?
10Base2:
It is an Ethernet term which means a maximum transfer rate of 10 Mbps that uses baseband signaling, with a contiguous cable segment length of 100 meters and a maximum of 2 segments.
10Base5:
It is an Ethernet term meaning a maximum transfer rate of 10 Mbps that uses baseband signaling, with 5 continuous segments not exceeding 100 meters per segment.
10BaseT:
It is an Ethernet term meaning a maximum transfer rate of 10 Mbps that uses baseband signaling and twisted pair cabling.
What is NIC?
– NIC stands for Network Interface Card.
– It is a peripheral card attached to a PC to helps it connect to a network.
– The MAC address of the card helps the network in identifying the PC.
What is the TTL (Time to Live)? Why is it required?
The time-to-live (TTL) is the number of hops that a packet is permitted to travel before being discarded by a router.
Explain the use of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP).
Internet Control Message Protocol is one of the important protocols in the Internet Protocol suite. It is mainly used in operating system of networked computers, for the purpose of sending error messages whether the destination is reachable or not. Ping command is the good example of using ICMP protocol.
What is Ping and Tracert?
Ping command is used to check the network connectivity.
Tracert command is used to trace the route of data packets.
Explain how NAT works.
Ans: NAT stands for Network Address Translation which translates public address into private address.
What is PPP protocol? Explain PPP packet format.
Ans: Point to Point protocol means direct connection between two pcs with a cable.
What are switches? Explain the concepts of Layer-3 switches.
Ans: Switch is a networking device which works in a layer 2 and layer 3 of OSI model. The roll of switch is to store, forward and broadcast. It can store MAC address of pcs. It has an inbuilt non-volatile memory which stores the Mac address temporarily. Once you turn off the switch it is going to erase all the Mac ids stored. Using switch you can send data to a particular pc. Here collision is less. There are two types of switch: catalyst and non catalyst.
Catalyst switch: It can be configured. You can divide the network of pcs connected to the same switch (able to create multiple segments).
Non catalyst switch: It cannot be configured. Here you cannot create multiple segments of network.
What is Router? Explain components of Routers.
Ans: Router is a networking device which works in a layer 3 of OSI model. It allows you to connect two different network.
Explain different layers in the OSI model.
Physical Layer:
Physical layer is the first layer of OSI model. All the physical connectivity takes place in this layer. It converts data unit to binary bits. The devices use in this layer are: hub, repeater, cables, etc.
Data Link Layer:
Data Link Layer is the second layer of OSI model. It converts binary bits into frame. The function of data link layer is physical address, flow control, error control and Mac addressing. The devices use in this layer is: switch, bridge and NIC.
Network Layer:
Network layer is the third layer of the OSI model. It converts frame into packets. The function of this layer is path determination, logical addressing and performs network routing functions. The devices use in this layer is: Router, Brouter. There is no use of network layer if all the devices connected to a single network.
Transport Layer:
Transport layer is the fourth layer of OSI model. It converts packets into segment. The function of transport layer is end-to-end connection, reliability and flow control.
Session Layer:
Session layer is the fifth layer of the OSI model. It converts segments into data. The function of session layer is interhost communication. It controls the connection between computers, establishes, manages and terminates the connections between the local and remote application and provides full-duplex, half-duplex or simplex operation.
Presentation Layer:
Presentation layer is the sixth layer of the OSI model. The main function of this layer is encryption, deception and compression.
Application Layer:
Application layer is the last layer of the OSI model. It is closest to the end user and interact directly with the software application.
Describe the concept of Subneting.
Ans: Subnetting is a process of dividing a large network into multiple small networks.
What is VLSM?
Ans: VLSM stands for Variable length subnet masking. Subnetting a subnet mask is called VLSM. It is use to avoid wastage of IP address.
What’s the difference Between an Intranet and the Internet?
Ans: Internet
1. Internet is wide network of computers and is open for all.
2. Internet itself contains a large number of intranets.
3. The number of users who use internet is Unlimited.
4. The Visitors traffic is unlimited.
5. Internet contains different source of information and is available for all.
Intranet
Intranet is the generic term for a collection of private computer networks within an organization. An intranet uses network technologies as a tool to facilitate communication between people or work groups to improve the data sharing capability and overall knowledge base of an organization’s employees. It is like Ethernet.
1. Intranet is also a network of computers designed for a specific group of users.
2. Intranet can be accessed from Internet but with restrictions.
3. The number of users is limited.
4. The traffic allowed is also limited.
5. Intranet contains only specific group information.
Define the term Protocol.
Ans: Protocol is a set of rules used by devices in a network to communicate with each other.
What is FTP (File Transfer Protocol)?
FTP is File Transfer Protocol. It used to exchange files on the internet. To enable the data transfer FTP uses TCP/IP, FTP is most commonly used to upload and download files from the internet. FTP also allows to update (delete, rename, move, and copy) files at a server. It uses a reserved port no 21.
What are network topologies? Explain Ring, Bus and Star topology.
A network topology describes the layout of a network. It describes how different nodes and elements are connected to each other. Different types of topology:
Ring Topology:
- All nodes connected with another in a loop.
- Each device is connected to one or more another device on either side.
- It uses token system for data transfer.
Bus Topology:
- All nodes connected to a central and a common cable called as a back bone.
- In bus topology, the server is at one end and the clients are connected at different positions across the network.
- Easy to manage and install.
- If the backbone fails, the entire communication fails.
Star Topology:
- All nodes connected to a central hub.
- The communication between the nodes is through the hub.
- Relative requires more cables as compared to BUS. However, if any node fails, it won’t affect the entire LAN.
What are Ping and Tracert?
Ping command is used to check the network connectivity.
Tracert command is used to trace the route of data packets.
What is NAT and why do we need NAT?
Ans: NAT stands for Network Address Translation and it is used to convert a private IP address into a public IP Address and a public IP Address into Private.
We use NAT because of the shortage of an IP address. IPv4 is a 32-bit address which has around 4,294,967,296 (4.2 Billion) IP addresses and the population in our beautiful world is more than 7 billion. Most of the users are using multiple devices too such as a smartphone, laptop, tab, desktop, etc. So, 4.2 Billion IP address is not sufficient for 7 billion of devices, right. For this reason, we use NAT (Network Address Translation).
What is PPP protocol? Explain PPP packet format.
Ans: Point to Point protocol means direct connection between two pcs with a cable.
What are switches? Explain the concepts of Layer-3 switches.
Ans: Switch is a networking device which works in a layer 2 and layer 3 of OSI model. The roll of switch is to store, forward and broadcast. It can store MAC address of pcs. It has an inbuilt non-volatile memory which stores the Mac address temporarily. Once you turn off the switch it is going to erase all the Mac ids stored. Using switch you can send data to a particular pc. Here collision is less. There are two types of switch: catalyst and non catalyst.
Catalyst switch: It can be configured. You can divide the network of pcs connected to the same switch (able to create multiple segments).
Non catalyst switch: It cannot be configured. Here you cannot create multiple segments of network.
What is Router? Explain components of Routers.
Ans: Router is a networking device which works in a layer 3 of OSI model. It allows you to connect two different network. There is no use of network layer if all the computers belong to the same network.
What are the basic components of routers?
Components of Router:
Internal components:
· ROM: Used to store the routers bootstrap details, operating system software.
· Flash memory: holds the operating systems images. The content is retained when the router is restarted.
· RAM: Used to store the Routing tables, configuration files, caching and buffering details. Content is lost when lost router is switched off or restarted.
· NVRAM: Stores the routers startup configuration files. Data is non-volatile.
· Network interfaces to connect router to network.
External components:
· Virtual terminals: For accessing routers
· Network management stations.
What is OSI Model?
Ans: OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection. It defines how data travels in a computer network. There are seven layers of OSI model:
· Application Layer
· Presentation Layer
· Session Layer
· Transport Layer
· Network Layer
· Data Link Layer
· Physical Layer
Explain different layers in the OSI model.
Physical Layer:
Physical layer is the first layer of OSI model. All the physical connectivity takes place in this layer. It converts data unit to binary bits. The devices use in this layer are: hub, repeater, cables, etc.
Data Link Layer:
Data Link Layer is the second layer of OSI model. It converts binary bits into frame. The function of data link layer is physical address, flow control, error control and Mac addressing. The devices use in this layer is: switch, bridge and NIC.
Network Layer:
Network layer is the third layer of the OSI model. It converts frame into packets. The function of this layer is path determination, logical addressing and performs network routing functions. The devices use in this layer is: Router, Brouter. There is no use of network layer if all the devices connected to a single network.
Transport Layer:
Transport layer is the forth layer of OSI model. It converts packets into segment. The function of transport layer is end-to-end connection, reliability and flow control.
Session Layer:
Session layer is the fifth layer of the OSI model. It converts segments into data. The function of session layer is interhost communication. It controls the connection between computers, establishes, manages and terminates the connections between the local and remote application and provides full-duplex, half-duplex or simplex operation.
Presentation Layer:
Presentation layer is the sixth layer of the OSI model. The main function of this layer is encryption, deception and compression.
Application Layer:
Application layer is the last layer of the OSI model. It is closest to the end user and interact directly with the software application.
Describe the concept of Subneting.
Ans: Subnetting is a process of dividing a large network into multiple small networks.
What is VLSM?
Ans: VLSM stands for Variable length subnet masking. Subnetting a subnet mask is called VLSM. It is use to avoid wastage of IP address.
What’s the difference Between an Intranet and the Internet?
Ans: Internet
1. Internet is wide network of computers and is open for all.
2. Internet itself contains a large number of intranets.
3. The number of users who use internet is Unlimited.
4. The Visitors traffic is unlimited.
5. Internet contains different source of information and is available for all.
Intranet
Intranet is the generic term for a collection of private computer networks within an organization. An intranet uses network technologies as a tool to facilitate communication between people or work groups to improve the data sharing capability and overall knowledge base of an organization’s employees. It is like Ethernet.
1. Intranet is also a network of computers designed for a specific group of users.
2. Intranet can be accessed from Internet but with restrictions.
3. The number of users is limited.
4. The traffic allowed is also limited.
5. Intranet contains only specific group information.
Define the term Protocol.
Ans: Protocol is a set of rules used by networking devices to communicate with each other.
What is FTP (File Transfer Protocol)?
FTP is File Transfer Protocol. It used to exchange files on the internet. To enable the data transfer FTP uses TCP/IP, FTP is most commonly used to upload and download files from the internet. FTP also allows to update (delete, rename, move, and copy) files at a server. It uses a reserved port no 21.
What is a network? What are the different types of network? Explain them
A network is a group of computers or nodes connected together.
Types of Networks:
LAN – Local Area Network connects a group of nodes covering a small physical area.
MAN: Metropolitan Area Network. It is basically used in cities. Example: cable TV.
CAN: Campus Area Network. It is basically use in school campus, colonies, etc.
WAN – Wide Area Network connects a group of nodes covering a wide area. WAN typically connects and allow communication between regions or national boundaries. The most common example of WAN is internet. .
What are network topologies? Explain Ring, Bus and Star topology.
A network topology describes the layout of a network. It describes how different nodes and elements are connected to each other. Different types of topology:
Ring Topology:
· All nodes connected with another in a loop.
· Each device is connected to one or more another device on either side.
· It uses token system for data transfer.
Bus Topology:
· All nodes connected to a central and a common cable called as a back bone.
· In bus topology, the server is at one end and the clients are connected at different positions across the network.
· Easy to manage and install.
· If the backbone fails, the entire communication fails.
Star Topology:
· All nodes connected to a central hub.
· The communication between the nodes is through the hub.
· Relative requires more cables as compared to BUS. However if any node fails, it won’t affect the entire LAN.
What is multicasting?
Multicasting allows a single message to be sent to a multiple group of recipients.
Explain the functionality of PING.
Ans: PING stands for Packet Internet Groper, it is use to check the connectivity between pc available in a network.
Define Telnet
Telnet is the main Internet protocol for creating a connection to a remote server.
Define SMTP.
SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, a protocol used for sending e-mail messages between servers. Its port number is 25 and with SSL is 465.
What Is a MAC Address?
Ans: MAC address is the physical address of a hardware device.
What is VPN?
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. It creates a secure tunnel over a public network with the help of which you are able to securely transfer data over the internet. VPNs may allow employees to securely access a private network while located outside the office.
What is IP Address?
Ans: IP stands for Internet Protocol Address. It is an address of a device connected to a network. There are two types of IP address:What is IP address?
Private address: these IP addresses are used exclusively within a private network and not for public to see.
Public Address: these are registered IP addresses used for the public. These IP address used on the internet.
Difference between Static and Dynamic IP.
Ans: Static IP is also called as the permanent address assigned to each device in a network, whereas Dynamic IP, a temporary address assigned to the device via DHCP.
What is the difference between public and private IP?
Ans: Difference between public and private IP are:
A public IP is routable but Private IP Address is not routable.
Public IP need to be purchased but private IP is free.
A public IP is unique and cannot be used multiple times but private IP can be used multiple times in different network.
Define Address Resolution Protocol.
Ans: ARP is used to translate IP address into MAC address and MAC address into IP address.
What is Routing Protocol?
The routing protocol is the way to send routing information between any routers in an autonomous system.
Bridge vs switch?
| Difference between Bridge and Switch | |
| BRIDGE | SWITCH |
| Bridge works in data link layer of OSI model | Switch works in data link layer and network layer of osi model. |
| Bridge has only two ports | Switch has multiple numbers of ports. |
| Bridge is use to connect two lan segment using same topology. | Switch is use to connect devices in the same network. |
| Bridge can operate only in half duplex mode | Switch can operate in both half duplex and full duplex mode. |
| The performance of bridge is slower then switch | The performance of Switch is faster then bridge. |
What is a Router?
The router is a networking device used for connecting two different networks.
Define gateway
A gateway is a network point that provides entrance into another network.
What is a firewall?
The firewall in a computer network is a secured wall between public and the private network. It protects your internal network from the user of an external network. The firewall may consist of hardware or software or both.
What are the types of firewalls?
Ans: There are two types of firewall:
Software Firewall: It provides security only to a particular pc.
Hardware Firewall: It provides security for the entire network.
Proxy Server:
A proxy server is a server placed between a client computer and the Internet. Proxy Server provides network security, manage what users are surfing on the internet, block certain websites and improve network performance.
What is Data encryption?
Data encryption ensures data safety and very important for confidential or critical data. It converts data into cipher text and the people who want to read need a security key. It protect data from being read, altered or forged while transmission.
Explain the use of network interface card, NIC.
NIC stands for Network Interface Card is used to connect computer to an Ethernet network
Explain token ring technology.
In this technology, all the devices are arranged in a circle. A token moves around the circular network. A device waits for the token before it sends its frame. Once it receives token, it initiates transmission of its frame.
What is HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)?
HTTP or Hyper Text Transfer Protocol provides a set of rules to transfer files, videos, images over the World Wide Web. It uses a reserved port no 80.
What is the difference between TCP vs. UDP?
- TCP guarantees the delivery of data. UDP, on the other hand, does not guarantee delivery of data. TCP delivers messages in the order they were sent. UDP has no ordering mechanisms.
- In TCP data is sent as a stream while UDP sends data as individual packets.
- UDP is faster than TCP.
- TCP is a connection-oriented protocol while UDP is connectionless.
Explain User Datagram Protocol, UDP.
The UDP is a connectionless, unreliable service. UDP messages can be lost and duplicated.
Difference between TCP and UDP?
- TCP guarantees the delivery of data. UDP on the other hand does not guarantee delivery of data.
- TCP delivers messages in the order they were sent. UDP has no ordering mechanisms.
- In TCP data is sent as a stream while UDP sends data as individual packets. UDP is faster than TCP.
- TCP is a connection-oriented protocol while UDP is connectionless.
Why do we need a subnet mask?
A subnet mask allows identification of host part and network part of an IP address. Subnet mask can be used to find if an IP address is present on a subnet or not.
What is SSL?
SSL is Secured Socket Layer. SSL is used to establish a secured and an encrypted connection between a server and the browser. SSL is most commonly seen in payment and banking web sites.
What is a node?
Ans: Any device connected to a network called node.
What does a router do?
Ans: Router is use to connect two different network. It creates a routing table for the data to travel in a particular route.
What protocol can you use to automatically assign IP addresses?
Ans: DHCP.
How many logical drives is it possible to fit onto a physical disk?
Ans: Maximum of 24 logical drives. The extended partition can only have 23 logical drives.
What is the maximum length allowed for a UTP cable?
Ans: A single segment of UTP cable has an allowable length of 90 to 100 meters. This limitation can be overcome by using repeaters and switches.
Describe Network Topology?
Network Topology refers to the layout of a computer network. It shows how devices and cables are physically connected to the network.
What is VPN?
Ans: VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. It creates a secure tunnel over a public network with the help of which you are able to securely transfer data over the internet. VPNs may allow employees to securely access a private network while located outside the office.
Briefly describe NAT.
Ans: NAT stands for Network Address Translation and it is used to convert a private IP address into a public IP Address and a public IP Address into Private.
How many layers are there under TCP/IP?
Ans: There are four layers: the Network Layer, Internet Layer, Transport Layer and Application Layer.
What are proxy servers and how do they protect computer networks?
Ans: A proxy server is a server placed between a client computer and the Internet. Proxy Server provides network security, manage what users are surfing on the internet, block certain websites and improve network performance.
What is a private IP address?
Ans: Private IP addresses are assigned for use on intranets. These addresses are used for internal networks and are not routable on external public networks. These ensure that no conflicts are present among internal networks while at the same time the same range of private IP addresses are reusable for multiple intranets since they do not “see” each other.
Describe star topology and one disadvantage?
Ans: Star topology consists of a central hub that connects to nodes. This is one of the easiest to setup and maintain. There is one disadvantage if the centralized hub fails entire network will fail.
Write the ranges of private IP Addresses.
| CLASS | Starting IP Address | Ending IP Address | Subnet Mask |
| A | 10.0.0.0 | 10.255.255.255 | 255.0.0.0 |
| B | 172.16.0.0 | 172.31.255.255 | 255.255.0.0 |
| C | 192.168.0.0 | 192.168.255.255 | 255.255.255.0 |
What is tracert?
Tracert is a command used to trace the route of a data packets.
What is DHCP?
Ans: DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. Its main task is to automatically assign an IP address to the devices across the network..
What is the main job of the ARP?
Ans: The main task of ARP or Address Resolution Protocol is to translate IP address to a MAC address.
What is TCP/IP?
Ans: TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol. This is a set of protocol layers that is designed to make data exchange possible on different types of computer networks.
60) What is Ping?
Ans: Ping stands for Packet Internet Groper. It is a tool used in a network to check the connectivity of the device in a network.
62) What is DNS?
Ans: DNS stands for Domain Name System. The main function of this network service is to convert IP address to host name and host name to IP address.
What are the maximum networks and hosts in class A, B and C network?
For Class A, there are 126 possible networks and 16,777,214 hosts
For Class B, there are 16,384 possible networks and 65,534 hosts
For Class C, there are 2,097,152 possible networks and 254 hosts
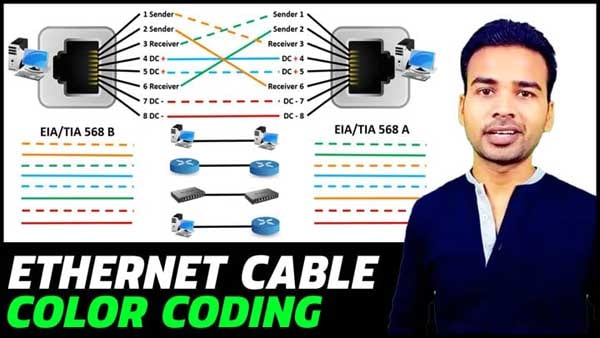
What is the color code of a straight-through cable?
| White of Orange | White of Orange |
| Orange | Orange |
| White of Green | White of Green |
| Blue | Blue |
| White Blue | White Blue |
| Green | Green |
| White of Brown | White of Brown |
| Brown | Brown |
What is the color code of a Cross over cable?
| White of Orange | White of Orange |
| Orange | Orange |
| White of Green | White of Blue |
| Blue | Green |
| White of Blue | White of Green |
| Green | Blue |
| White of Brown | White of Brown |
| Brown | Brown |
What is the color code of a Roll over cable?
| White of Orange | Brown |
| Orange | White of Brown |
| White of Green | Green |
| Blue | White of Blue |
| White of Blue | Blue |
| Green | White of Green |
| White of Brown | Orange |
| Brown | White of Orange |
What is ipconfig?
Ans: Ipconfig is a command that is commonly used to identify the addresses information of a computer on a network. It can show the physical address as well as the IP address.
What is the difference between a straight-through and crossover cable?
Straight-through cable: is used to connect computers to a switch, hub or router.
Crossover cable: is used to connect two similar devices together, such as a PC to PC or Hub to hub.
Roll over cable: is use to connect pc to a console port of a router. Using this you can configure router from pc.
When you move the NIC cards from one PC to another PC, does the MAC address gets transferred as well?
Ans: Yes, that’s because MAC addresses are hard-wired into the NIC circuitry, not the PC. This also means that a PC can have a different MAC address when the NIC card was replaced by another one.
What is the role of IEEE in computer networking?
Ans: IEEE stands for Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, is an organization composed of engineers that issues and manages standards for electrical and electronic devices. This includes networking devices, network interfaces, cablings and connectors.
94) What protocols fall under the TCP/IP Internet Layer?
Ans: There are 4 protocols that are being managed by this layer. These are ICMP, IGMP, IP and ARP.
What ports are used by DHCP and the DHCP clients?
Ans: DHCP server port number is 67 and DHCP client port number is 68.
How will you test LAN card?
Ans: Ping 127.0.0.1 , If getting reply it is working fine
What is the difference between DOMAIN and WORKGROUP?
Workgroup:
- Every PC is responsible for its security own.
- No centralize administration
- Main aim to save hardware recourse
- Best suite in school, training institute, cyber café
Domain: –
- Server is responsible for data safety.
- Centralize administration
- Main aim is to secure data
- Best suite in company environments
Which command is used to check the IP address of your system?
Ans: Ipconfig
What is Proxy Server?
Ans: A proxy server is a server placed between a client computer and the Internet. Proxy Server provides network security, manage what users are surfing on the internet, block certain websites and improve network performance.
What is full form of C.M.O.S ?
Ans: the Complementary metal oxide semiconductor
What is IP Address?
Ans: IP stands Internet Protocol Address. It is a unique address of a node in the network.
What is Difference between STP and UTP?
STP cable is mostly used by IBM; it has an extra cover over each pair.
UTP cable is used in a star topology. It has a single cover over all pair.
Full form of ping.
Ans: PING stand for Packet Internet Groper
What are the minimum requirements for xp installation?
64MB RAM
1.5GB free HDD space
233MHz minimum processor.
What are 10Base2, 10Base5 and 10BaseT Ethernet LANs?
10Base2— An Ethernet term meaning a maximum transfer rate of 10 Megabits per second that uses baseband signaling, with a contiguous cable segment length of 100 meters and a maximum of 2 segments.
10Base5—An Ethernet term meaning a maximum transfer rate of 10 Megabits per second that uses baseband signaling, with 5 continuous segments not exceeding 100 meters per segment.
10BaseT—An Ethernet term meaning a maximum transfer rate of 10 Megabits per second that uses baseband signaling and twisted pair cabling.
What is public IP address?
Ans: A public IP address is an address leased from an ISP that allows or enables direct Internet communication.
What’s the benefit of subnetting?
Reduce the size of the routing tables.
Reduce network traffic. Broadcast traffic can be isolated within a single logical network.
Provide a way to secure network traffic by isolating it from the rest of the network.
What are the differences between static ip addressing and dynamic ip addressing?
With static IP addressing, a computer (or other device) is configured to always use the same IP address. With dynamic addressing, the IP address can change periodically and is managed by a centralized network service
What is APIPA?
Automatic private IP addressing (APIPA) is a feature mainly found in Microsoft operating systems. APIPA enables clients to still communicate with other computers on the same network segment until an IP address can be obtained from a DHCP server, allowing the machine to fully participate on the network. The range of these IP address are the 169.254.0.1 to 169.254.255.254 with a default subnet mask of 255.255.0.0.
Which command will you use to find out the name of the pc in networks?
Ans: NSLOOKUP
What is router?
Ans: Router is a networking device works in the network layer of OSI Model used to connect two or more different networks.
ISO stand for?
Ans: International standard organization
OSI stand for?
Ans: Open System Interconnection
What is topology?
Ans: A topology defines the layout how devices are connected in a network.
How many types of topology are available?
A point-to-point topology has a single connection between two devices.
In a star topology, a central device has many point-to-point connections to other devices.
A bus topology uses a single connection or wire to connect all devices.
In a ring topology, device one connects to device two, device two connects to device three, and so on to the last device, which connects back to device one.
Which OSI layer does IP belong?
Ans: IP belongs to the Network Layer (layer 3) of OSI model.
What is a subnet mask?
Ans: Subnet mask is a 4 byte (32 bit) number used to identify the sub-network ID and the host ID from an IP address. All the hosts in a sub-network will have the same subnet mask.
Mention what is the difference between the switch, hub, and router?
| HUB | SWITCH | ROUTER |
| Hub is a broadcast device. | Switch is a multicast device. | Router is a routing device. |
| Hub works in physical layer of OSI model. | Switch works in data link layer and network layer of OSI model. | Router works in network layer of OSI model. |
| Hub is use to connect devices in the same network. | Switch is use to connect devices in the network. | Router is use to connect two different network. |
| Hub sends data in the form of bits. | Switch sends data in the form of frames. | Router sends data in the form of packets. |
| Hub works in half duplex. | Switch works in full duplex. | Router works in full duplex. |
| Only one device can send data at a time. | Multiple devices can send data at a time. | Multiple devices can send data at a time. |
| Hub does not store any MAC address of a node in the network. | Switch stores the IP Address and MAC address of nodes used in a network. | Router stores the IP Address and MAC address of nodes used in a network. |
Mention what is the size of IP address?
Ans: Size of IP address is 32 bit for IPv4 and 128 bit for IPv6.
Mention what are the ranges for the private IPS?
Ans: Ranges for private IPS are
- Class A: 10.0.0.0 – 10.0.0.255
- Class B: 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.0.0
- Class C: 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.0.255
In how many ways you can access router?
Ans: You can access it in three ways
- Telnet (IP)
- AUX (Telephone)
- Console (Cable)
Mention what is the difference between TCP and UDP?
Ans: TCP and UDP both are protocols for sending files across computer network
| TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) | UDP (User Datagram Protocol) |
| TCP is connection oriented protocol. When connection lost during transferring files, the server would request the lost part. While transferring a message, there is no corruption while transferring a message | UDP is based on connectionless protocol. When you send data, there is no guarantee whether your transferred message will reach there without any leakage |
| The message will deliver in the order it is sent | The message you sent may not be in the same order |
| Data in TCP is read as a stream, where one packet ends, and another begins | Packets are transmitted individually and are guaranteed to be whole if they arrive |
| Example of TCP includes World Wide Web, file transfer protocol, e-mail, | Example for UDP are VOIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol) TFTP ( Trivial File Transfer Protocol),Explain the difference between half-duplex and full-duplex? |
Full duplex means that the communication can occur in both directions at the same time, while half duplex means that the communication can occur in one direction at time.
What are routing protocols? Give example.
Ans: Routing protocol is a protocol that specifies how routers communicate with each other to disseminate information that allows them to select routes between any two nodes on a network.
IGRP (Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
IS-IS (Intermediate System to Intermediate System)
How do I know the path that a packet takes to the destination?
Ans: use “tracert” command-line
What is RIP (Routing Information Protocol)?
Ans: It is a simple protocol used to exchange information between the routers.
107: You want to be sure your PC is connected to the network. What you should do?
Ans: ping the server
115: What is another name for twisted pair cable?
Ans: 10baseT
What protocol do you use to transfer a file over the Internet?
Ans: FTP
How many pins does a SVGA monitor cable have?
Ans: 15
At the end of a SCSI chain you should use a terminator. This terminator is actually what?
Ans: a resistor
What computer chip holds the computer’s configuration information?
Ans: CMOS
What does CMOS stand for?
Ans: Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor.
What does the term BIOS stand for?
Ans: Basic Input/output System
What is CISC and RISC?
| CISC | RISC |
| Complex Instruction Set Chip | Reduced Instruction Set Chip |
| CISC chips have an increasing number of components | RISC chips have fewer components and a smaller instruction set |
| CISC chips do all of the processing themselves | RISC chips distribute some of their processing to other chips |
| Computers typically use CISC | tablets, smart phones and other devices use RISC |
| CISC implementations tend to be slower than RISC implementations. | RISC implementations tend to be faster than SISC implementations. |
What is Hyper Threading?
Ans: Hyper Threading is technology use by Intel processor which acts single processor to be act as a multiple processor. It helps in multitasking.
Difference between SATA and PATA
| SATA | PATA |
| SATA stands for Serial Advanced Technology Attachment | PATA stands for Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment |
| SATA is the latest version we use now a days | PATA is older technology |
| SATA is much faster than PATA | |
| SATA does not uses a slave/master arrangement. | PATA uses a slave/master arrangement while SATA does not |
| SATA uses smaller cables than PATA | PATA uses longer cables than SATA |
| The speed is 600 MB/s | The speed is 133 MB/s |
| It required 0.25 volts | It required 5 volts |
What is SCSI?
Ans: SCSI is Small Computer System Interface, is a type of interface used for computer components such as hard drives, optical drives, scanners and tape drives. SCSI is a faster, more robust technology than IDE and SATA, and has traditionally been utilized in servers. It can connect up to 15 devices to your computer.
What is SMPS?
Ans: SMPS stands for Switching Mode Power Supply. It converts AC to DC and provides power to all the components of a PC.
Difference between FAT and NTFS?
| NTFS | FAT |
| New Technology File System | File Allocation Table |
| Supports file encryption | Does not support encryption |
| Supports compression | Does not support compression |
| NTFS cannot be converted to FAT. | FAT can be converted to NTFS. |
| Supports partition greater than 32 GB. | Does not support partition greater than 32 GB. |
| NTFS supports longer file name than FAT. | FAT supports small file name than NTFS. |
| NTFS allows you to set permissions on local files and folders as well. | FAT does not provide security over locally logged-on users |
| NTFS is more secure than FAT32 | FAT is less secure than NTFS |
| NTFS supports disk quota. | FAT does not support disk quota. |
What would you check if there is no sound from your computer? (Audio not working)
1. Check for cable connections
2. Check for power to the speakers
3. Check for volume control
4. Check for device drivers
What does the term USB stand for?
Ans: USB stands for Universal Serial Bus.
What is DNS?
Ans: DNS stands for Domain Name System. It is used to translate a domain name (e.g. www.google.com) into an IP Address(192.168.10.1) or vice versa. It is very difficult to remember an IP Address of all the website. So, we use DNS Server which helps us to convert a website name into an IP Address and allow us to access the website.
What are RJ45 and RJ11 connectors?
Ans: RJ45 connectors are used for LAN/Ethernet connections and RJ11 connectors are used for Telephone Cable connections.
What are the possible ways of data exchange?
Simplex: is a communication channel that sends information only in one direction. Example: Television or Radio.
Half duplex: allowing the transmission of signals in both directions but not simultaneously (at a time). Example: Walkie Talkie.
Full duplex: Refers to the transmission of data in two directions simultaneously. Example: telephone.
What is MAC Address?
Ans: MAC stands for Media Access Control, it is the physical address of a device and MAC address is usually stored in ROM on the network adapter card and is unique.
Destination host unreachable vs Request timeout
Destination host unreachable means there is no proper route defined between two hosts.
Request time out means the ICMP packet reached from one host to the other host but the reply could not reach the requesting host. This can be due to many different causes; the most common include failure of the ARP request, packet filtering, routing error, etc.
How to solve Destination host unreachable?
Ans: Check whether the cables are properly connected.
Check the IP address.
Check the Default gateway and subnet mask on both the pc. it should be same.
Disable the firewall and check whether the issue is resolved.
Type the command ipconfig/release and ipconfig/renew. And check whether the issue is resolved.
Perform a tracert to the destination IP and check where the problem lies.
Check whether the router is properly configured and update the routing table.
While pinging the Google get error ‘Request timeout’, how to solve?
Open cmd prompt and type
Check the ip address of both the pc using command ipconfig/all.
Ping google.com
Ipconfig /flushdns
netsh int ip reset
What is the difference between Windows XP and Windows 7?
- The shutdown and the startup is very fast in Windows 7 when compared to the Windows XP
- We have bit locker in win 7 but not in win XP.
- We have IP version 6 in win 7 but not in win XP.
- Win XP does not have any gadget like clock, weather, etc.
- Win7 provides diagnose tools for troubleshooting.
- Windows Aero (3D visuals) available in Win 7.
- Application Compatibility mode is available in win 7 but not in Win XP.
- Remote Assistant available in Win 7 not in Win XP.
- Disk shrinking and extending options are available in Windows 7
- Automatic Driver detection when the new device connected.
What is different between Win 7 and Win 8?
- Windows 8 startup is very fast compared to windows 7.
- When you log in to Windows 8, the first screen you see is the new ‘Start Screen’, also known as ‘Metro’.
- Windows 8 doesn’t have a Start Menu. Instead, it has a ‘Charms’.
- Windows 8 has an app called windows store from where you can download many apps.
- Windows 8 has a new ‘Mail’ app, where you can configure multiple mail accounts.
- Windows 8 comes with an antivirus program called ‘Windows Defender’.
- Instead of having separate contacts for email, Skype and social networking e.g. Facebook, you will find all your contacts together in the new ‘People’ app.
- You can pause a copy operation in the middle of it.
- You will get the ribbon interface in windows explorer like we have seen in MS office 2007.
- Two cool new features of Windows 8 are the refresh and reset options. Reset will remove all your personal data, apps, and settings and reinstall Windows. Refresh will keep all data, apps and settings and reinstall Windows.
- Here you can sign in using windows live id in windows 8.
- You can do multiple tasks in single windows by splitting it.
What is different between Win 8 and Win 10?
- In new windows 10, the start menu is back.
- Here you will find a new Cortana which helps you like a personal assistant.
- In windows 10 you will get the all-new virtual desktop feature.
- Windows 10 comes with DirectX 12 which helps in better gaming performance.
- You can play XBOX games in windows 10.
- Windows 10 is introducing the new browser called Spartan.
- You will get search bar in the task manager itself.
Difference between IPv4 and IPv6.
| IPv4 | IPv6 |
| IPv4 addresses are 32-bit length. | IPv6 addresses are 128-bit length. |
| IPv4 addresses are binary numbers represented in decimals. | IPv6 addresses are binary numbers represented in hexadecimal. |
| IPv4 has 5 classes of IP address. | IPv6 has no classes. |
| IPv4 has limited number of IP address | In IPv6 you can create the unlimited number of IP address. |
| In IPv4 bits are separated by . (dot). | In IPv6 bits are separated by : (colon). |
| It supports VLSM. | It does not support VLSM. |
| Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is available to map IPv4 addresses to MAC addresses. | Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is replaced with a function of Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP). |
| The checksum field is available in IPv4 header. | No checksum field in IPv6 header. |
| IPSec support is only optional. | Inbuilt IPSec support. |
| Fragmentation is done by sender and forwarding routers. | Fragmentation is done only by the sender.
|
| Broadcast messages are available. | Broadcast messages are available. |
Network protocols and their port number:
| Protocols | Port No |
| FTP | 21 |
| TELNET | 23 |
| HTTP | 80 |
| DNS | 53 |
| SSH (Secure Shell) | 22 |
| SMTP | 25 |
| DHCP Server | 67 |
| DHCP client | 68 |
| POP3 (Post Office Protocol, version 3) | 110 |
| NTP (Network Time Protocol) | 123 |
| IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) | 143 |
| SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) | 161 |
| IMAP3 (Internet Message Access Protocol 3) | 220 |
| SSL (Secure Socket Layer) | 443 |
| NetBIOS (Network Bios) | 139 |
| RIP (Routing Information Protocol) | 520 |
Name the protocol used for terminal services?
Ans: RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol)
What is DHCP?
Ans: DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Control Protocol. It is used to automatically provide the IP address to the clients.
What is DNS?
Ans: DNS stands for Domain Name System. It translates the domain name into IP address and IP address into host name.
What is a firewall?
Ans: The firewall in a computer network is a secured wall between public and the private network. It protects your internal network from the user of an external network. The firewall may consist of hardware or software or both.
What is WAN?
Ans: WAN stands for Wide Area Network that covers a large geographical area using leased telecommunication lines.
Define network gateway?
A gateway is a network point that acts as an entrance to another network.
What is pooling?
Ans: Print pool enables you to make the group of printer. Suppose you make group of 5 printer. While printing it detect the free printer automatically.
Define OSI model?
Ans: OSI stands for Open System Interconnection. It has seven layers which perform different task.
| OSI Layer | Protocols | Devices use | Function | |
| 7 | Application | FTP, SMTP, TELNET, DHCP, POP3, HTTP, etc | Resources sharing, Remote File Access, Remote printer access. Its data unit is Data. | |
| 6 | Presentation | SSL, | Data compression, encryption and decryption. Its data unit is Data. | |
| 5 | Session | TCP, RTP | Allows session establishment between processes running on different station. | |
| 4 | TRANSPORT | TCP, UDP | It converts packets into segments. Its data unit is segment. | |
| 3 | Network | IP, IPSec, ICMP, IGMP, OSPF | Router and Brouter | It converts frame into packets. Its data unit is packet and datagram. |
| 2 | Data Link | PPP, PPTP, SLIP | Switch, Bridge and NIC | It converts binary bits into frame. Its function is: physical addressing, flow control, error control and MAC addressing. |
| 1 | Physical | HUB, Repeater and cables. | All the physical connectivity takes place in this layer. It converts data unit into binary bits. Its data unit is binary bit. |
What is Active Directory?
Ans: Active Directory is a centralized and standardized system that arranges all the network user, computer and object into a logical hierarchical group. It has information about all the object: users, computers, resources like printer, shared files/folder in an organizations network.
Difference between POP and IMAP?
| POP3 | IMAP |
| POP stands for Post Office Protocol | IMAP stands for Internet Message Access Protocol |
| POP3 port number is 110 and 995 (SSL) | IMAP port number is 143 and 999 (SSL) |
| This protocol is not sync with web server | This protocol is always in sync with the web server |
| To read the mail it needs to be downloaded first. | To read the mail it need not to be downloaded as you can access it online from the web server. |
| Mails can be accessed only from a single device. | Mails can be accessed from any device as you need to login to the web server. |
| The user cannot organize mails in the mailbox of the mail server. | The user can organize the emails on the server. |
| The user cannot create, delete or rename mailboxes on a mail server. | The user can create, delete or rename mailboxes on the mail server. |
| Any changes you make in the mail client (Outlook, Thunderbird) is not going to replicate to the web server. | Any changes you make in the mail client (Outlook, Thunderbird) it always replicates to the web server. |
| Mails are download in local PC and can be accessed locally without internet. | Mails are always on the server and it required internet to access them. |
Why we use DNS Server?
Ans: DNS Server is used to translates the domain name into IP address and IP address into domain name.
Difference between TCP and UDP:
| TCP | UDP |
| TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol. | UDP stands for User Datagram Protocol. |
| TCP is connection oriented protocol, which means that every time a packet is sent say from host A to B. We will get an acknowledgment. | UDP is User Datagram Protocol. Here we are not receiving any confirmation. |
| Use by protocols HTTP, HTTPs, FTP, SMTP, Telnet | Use by protocols DNS, DHCP, TFTP, SNMP, RIP, VOIP. |
| The speed for TCP is slower than UDP. | UDP is faster because there is no error-checking for packets. |
| TCP header size is 20 bytes | UDP Header size is 8 bytes. |
| TCP does error checking | UDP does error checking, but no recovery options. |
| If you send two messages along a connection, one after the other, you know the first message will get there first. You don’t have to worry about data arriving in the wrong order. | If you send two messages out, you don’t know what order they’ll arrive in i.e. no ordered |
| It is used while sending files, mails, etc. | It is use while playing online games. |
| It is use to send large amount of data. | It is use to send small amount of data. |
Difference between hub, switch and router?
| HUB | SWITCH | ROUTER |
| Works in layer 1 (Physical layer) | Works in Layer 2 (Data Link Layer) | Works in Layer 3 (Network Layer) |
| Basically, use in Bus Topology | Basically use in Star Topology. | It is used to connect to different networks. |
| It broadcast data (sending data to all). | Switch is a multicast device. | Routers maintain routing table for data forwarding. |
| Hubs work only in half duplex mode. | Switches, unlike hubs, support full duplex. | Router supports full duplex. |
| If more than one device sends out data simultaneously then data collisions happen. | More than one device can send data. | More than one device can send data. |
| Switching protocols: PPP, PPTP, SLIP | Routing protocol: IP, IPSec, ICMP, IGMP, OSPF | |
| Hub cannot be configured. | Switch can be configured. | Router can be configured. |
| Hub is a device which transmits binary bits along networks. | Switch is a device which transmits frames along networks. | Router is a device which transmits data packets along networks. |
Write some features of a hub, switch and router?
Ans: Features of HUB:
- Hubs operate in layer 1 of OSI model and is used to connect network devices for communication.
- Hubs work only in half-duplex mode I.e. a device connected to a hub can either send or receive data at a given time.
- If more than one device sends out data simultaneously then data collisions happen.
- HUB is a broadcast device.
Features of a switch:
- Switches are network devices that operate on layer-2 of OSI model
- Switches are also known as intelligent hubs.
- Switches, unlike hubs, support full duplex data transfer communication for each connected device.
- Switching protocols: PPP, PPTP, SLIP
Features of Router:
- Routers are the network devices that operate at Layer-3 of OSI model of communication.
- It is used to connect two different networks.
- The routing protocols are: IP, IPSec, ICMP, IGMP, OSPF.
- Sometimes routers are also known as layer-3 switches.
- Routers maintain a routing table for data forwarding.
What is ARP and RARP?
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol). It is used to convert IP address to MAC address.
RARP (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol). It is use to convert MAC address to IP address.
What is the DHCP default lease period?
Ans: DHCP duration of an IP address is leased for 8 days by default.
What is subnet mask?
Ans: A Subnet mask is a 32-bit number that masks an IP address, and divides the IP address into network address and host address.
What is Ethernet?
Ans: Ethernet is a private network. Example LAN and MAN.
What is RAID? Define level.
Ans: RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent (or Inexpensive) Disks. RAID is a collection of hard drives joined together for speed and fault tolerance.
RAID 0 – based on striping. This RAID level doesn’t provide fault tolerance but increases the system performance (high read and write speed).
RAID 1 – utilizes mirroring technique, increases read speed in some cases and provides fault tolerance in the loss of no more than one member disk.
RAID 0+1 – based on the combination of striping and mirroring techniques. This RAID level inherits RAID 0 performance and RAID 1 fault tolerance.
RAID 5 – utilizes both striping and parity techniques. Provides the read speed improvement as in RAID 0 approximately, survives the loss of one RAID member disk.
RAID 6 – similar to RAID 5 but uses two different parity functions. The read speed is the same as in RAID 5.
What is BIOS?
Ans: BIOS stands for Basic Input Output System. It controls all the input and devices in a PC.
What is CMOS?
Ans: CMOS stands for Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor. It is used to update date and time of your system.
What is IRQ?
Ans: IRQ stands for Interrupt Request are hardware lines over which devices can send interrupt signals to the microprocessor.
What is Domain Controller?
Ans: A domain controller is a server that is running a version of the Windows Server operating system and has Active Directory Domain Services installed. It performs a function of user authentication and maintains the security policy for the domain.
What is Domain?
Ans: A domain is a subnetwork made up of a group of clients and server under the control of one centralized security database called domain controller. Domain work on server clients configuration. Here only domain acts as a server and provides user accounts to clients and clients act as a dumb terminal.
How to configure member of domain?
Ans: Right click on my computer and go to properties
Click on Change settings
Change pc name
Click on the member of domain and type the domain name.
Restart your computer and try to login to your domain account.
How to remove your PC from a domain?
Ans: Right click on My computer and go to properties.
Click on change settings
Change PC name.
Select Workgroup and save.
Restart your computer.
Types of IP address?
Ans: APIPA (Automatic Private Internet Protocol Address). APIPA assigns a class B IP address from 169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255 to the client when a DHCP server is either permanently or temporarily unavailable.
Public IP Address use in the internet.
Private IP Address used in a private network:
| Class | Private IP Address Range | Default Subnet Mask |
| A | 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 | 255.0.0.0 |
| B | 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 | 255.255.0.0 |
| C | 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 | 255.255.255.0 |
What is loopback IP address?
Ans: Loopback address is an IP address (127.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255) which is use to check whether your NIC is working or not.
What is Network?
Ans: Network is an interconnection between two or more computers or devices.
What is internet?
Ans: The world largest network is called the internet.
What is an operating system?
Ans: An operating system (OS) is the first software loaded on a computer that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs.
What is SMPS?
Ans: SMPS stands for switched-mode power supply. It converts AC to DC and provides power to all the components of a pc.
What is FQDN?
Ans: An FQDN contains (fully qualified domain name) both the hostname and a domain name. It uniquely identifies a host within a DNS hierarchy
What is DHCP scope?
Ans: A scope is a range, or pool, of IP addresses that can be leased to DHCP clients on a given subnet.
How do I clear the DNS cache on the DNS server?
Ans: To clear DNS Cache do the following:
- Start
- Run
- Type “cmd” and press enter
- In the command window type “ipconfig /flushdns”